Setting up a Kubernetes Cluster the Hard Way with kubeadm (GitOps Series, Part 3)
Published:
Setting up a Kubernetes Cluster the Hard Way with kubeadm (GitOps Series, Part 3)
| ← Part 1: Setting up the Kubernetes cluster | ← Part 2: Core Infrastructure and Tools |
In the previous parts of this series, we set up a Kubernetes cluster from scratch using kubeadm (Part 1) and deployed essential infrastructure components and tools (Part 2). Now it’s time to put everything together and deploy actual applications using the App of Apps pattern with ArgoCD.
This post covers:
- The App of Apps pattern with ArgoCD ApplicationSets
- CloudNative-PG for PostgreSQL databases
- Tailscale Operator for secure remote access
- Kyverno policies for automatic Tailscale ingress generation
- Immich as a self-hosted Google Photos replacement
- CouchDB for Obsidian sync
Prerequisites
- Completed Part 1 and Part 2
- ArgoCD with ApplicationSets configured
- Vault with External Secrets Operator
- SMB or NFS share for persistent storage
Find all configurations in my homelab repository.
The App of Apps Pattern with ArgoCD
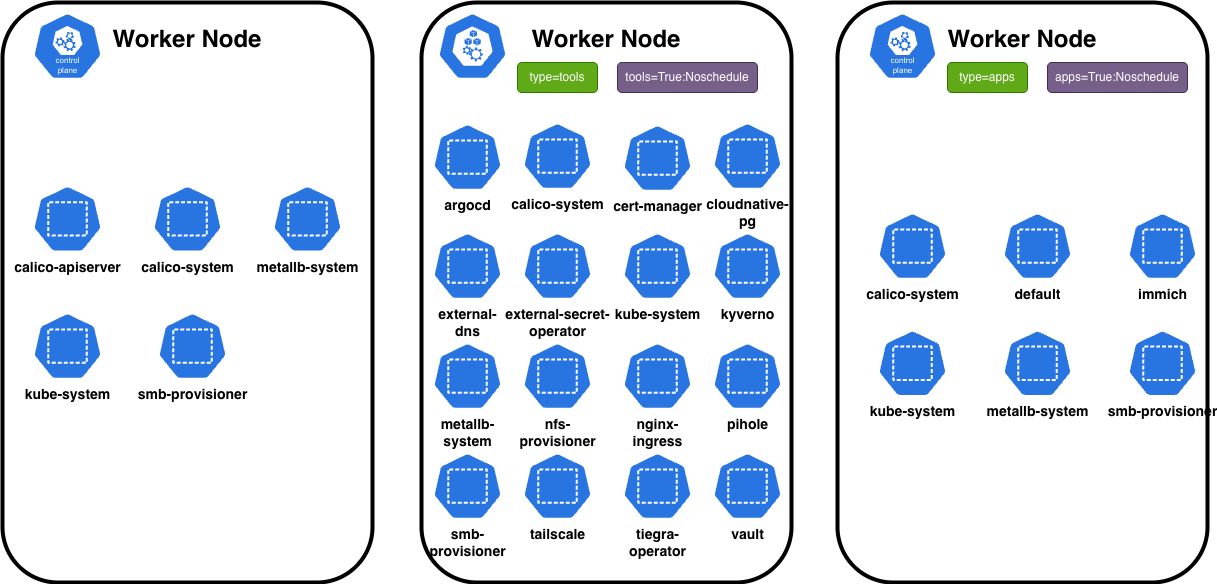
In Part 2, we set up ArgoCD with ApplicationSets that use a GitGenerator to automatically discover and deploy applications. This pattern allows us to add new applications simply by creating a folder with the necessary manifests and an app.yaml file.
Repository Structure
homelab/
├── apps/ # Application workloads (scheduled on wp2)
│ ├── couchdb/
│ ├── immich/
│ ├── netshoot/
│ └── postiz-app/
├── core/ # Core infrastructure (all nodes)
│ ├── calico/
│ ├── metallb-system/
│ └── metrics-server/
├── tools/ # Tools and operators (scheduled on wp1)
│ ├── argocd/
│ ├── cert-manager/
│ ├── cloudnative-pg/
│ ├── external-dns/
│ ├── external-secret-operator/
│ ├── kyverno/
│ ├── nginx-ingress/
│ ├── pihole/
│ ├── tailscale/
│ ├── vault/
│ └── wildcard-tls/
└── helmCharts/ # Cached helm charts for offline use
Application Definition Pattern
Each application includes an app.yaml file that ArgoCD’s ApplicationSet reads:
# apps/immich/app.yaml
name: immich
path: apps/immich
namespace: immich
project: default
The ApplicationSet creates ArgoCD Applications for each discovered app.yaml:
# tools/argocd/appSets/apps.yaml
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: ApplicationSet
metadata:
name: apps-appset
spec:
goTemplate: true
goTemplateOptions: ["missingkey=error"]
generators:
- git:
repoURL: https://github.com/NovoG93/homelab
revision: main
files:
- path: "apps/**/app.yaml"
template:
metadata:
name: "{{ .name }}"
labels:
group: apps
spec:
project: "{{ .project }}"
source:
repoURL: https://github.com/NovoG93/homelab
targetRevision: main
path: "{{ .path.path }}"
destination:
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
namespace: "{{ .namespace }}"
syncPolicy:
automated:
prune: true
selfHeal: true
syncOptions:
- CreateNamespace=true
- PrunePropagationPolicy=foreground
- ApplyOutOfSyncOnly=true
- ServerSideApply=true
Note the key differences from the tools-appset:
- Automated sync: Apps have
automated.prune: trueandselfHeal: truefor fully automated GitOps - Group label: Apps are labeled with
group: appsfor easy filtering in the ArgoCD UI
CloudNative-PG for PostgreSQL
The CloudNative-PG operator manages PostgreSQL clusters as Kubernetes-native resources. The operator runs on wp1 (tools), while database pods run on wp2 (apps) alongside their applications. I use CloudNative-PG for Immich’s database.
Tailscale Operator for Remote Access
Tailscale provides zero-config VPN access to your homelab. The operator automatically creates Tailscale ingresses for services. For this I set up a kyverno policy that generates Tailscale ingresses from nginx-ingress VirtualServer resources.
Automatic Tailscale Ingress with Kyverno
Instead of manually creating Tailscale ingresses, I use a Kyverno ClusterPolicy that automatically generates them from VirtualServer resources:
# tools/kyverno/clusterPolicies/create-tailscale-ingress-from-virtualserver.yaml
apiVersion: kyverno.io/v1
kind: ClusterPolicy
metadata:
name: create-tailscale-ingress-from-virtualserver
spec:
validationFailureAction: Enforce
useServerSideApply: true
rules:
- name: create-tailscale-ingress-from-virtualserver
skipBackgroundRequests: false
match:
any:
- resources:
kinds:
- k8s.nginx.org/v1/VirtualServer
exclude:
any:
- resources:
kinds:
- k8s.nginx.org/v1/VirtualServer
selector:
matchLabels:
ignore-ts: "true" # Add this label to skip Tailscale ingress
generate:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
name: tailscale-{{request.object.metadata.name}}-ig
namespace: "{{request.object.metadata.namespace}}"
synchronize: true
generateExisting: true
data:
metadata:
annotations:
created-by: kyverno.io/create-tailscale-ingress-from-virtualserver
tailscale.com/proxy-class: "tool-node-config"
labels: "{{ request.object.metadata.labels || parse_json('{}') }}"
spec:
ingressClassName: tailscale
tls:
- hosts:
- "{{request.object.metadata.name}}-{{request.object.metadata.namespace}}"
rules:
- http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: "{{request.object.spec.upstreams[0].service}}"
port:
number: "{{request.object.spec.upstreams[0].port}}"
This policy:
- Watches for any VirtualServer resource creation
- Generates a corresponding Tailscale Ingress automatically
- Uses the
tool-node-configProxyClass to ensure proxies run on the tools node - Can be skipped by adding the
ignore-ts: "true"label to a VirtualServer
Now every application with a VirtualServer automatically gets both:
- Local access via nginx-ingress + Pi-hole DNS (e.g.,
immich.novotny.live) - Remote access via Tailscale (e.g.,
immich-immichon your tailnet)
Deploying Immich
Immich is a self-hosted Google Photos replacement. The deployment consists of:
- immich-server: Main API server
- immich-machine-learning: Face recognition and search
- valkey: Redis-compatible cache
- PostgreSQL: CloudNative-PG with vector extensions
- SMB storage: Photo/video library on NAS
PostgreSQL with Vector Extensions
# apps/immich/cloudnative-pg/pg-db.yaml
apiVersion: postgresql.cnpg.io/v1
kind: Cluster
metadata:
name: immich-postgres
spec:
instances: 1
imageName: ghcr.io/tensorchord/cloudnative-vectorchord:16.9-0.4.3
postgresql:
shared_preload_libraries: ["vchord.so"]
bootstrap:
initdb:
database: immich-db
owner: immich
secret:
name: immich-database-credentials
postInitApplicationSQL:
- CREATE EXTENSION vchord CASCADE;
- CREATE EXTENSION earthdistance CASCADE;
# ... storage and affinity config in repo
Deploying CouchDB for Obsidian Sync
CouchDB provides self-hosted sync for Obsidian via the LiveSync plugin.
Key configuration points:
- CORS enabled: Required for Obsidian to connect
- Allowed origins:
app://obsidian.md,capacitor://localhost - Auto-setup: Creates system databases and personal vault
- Credentials from Vault: Via ExternalSecret
Summary
| Component | Purpose |
|---|---|
| App of Apps Pattern | GitGenerator scans for app.yaml files |
| CloudNative-PG | Kubernetes-native PostgreSQL |
| Tailscale Operator | Zero-config VPN with auto-provisioning |
| Kyverno Policy | Auto-generates Tailscale ingress from VirtualServers |
| Immich | Self-hosted Google Photos |
| CouchDB | Self-hosted Obsidian sync |
The Complete Picture
With all three parts completed, we now have:
- Kubernetes Cluster (Part 1): kubeadm-bootstrapped with control plane and workers
- Infrastructure (Part 2): Networking, storage, secrets, certificates, and GitOps
- Applications (Part 3): Self-hosted services with automated deployment
The beauty of this setup:
- Adding a new app: Create folder with manifests and
app.yaml→ ArgoCD deploys it - Updating an app: Push to Git → ArgoCD syncs automatically
- Secret management: Add to Vault → ESO syncs to Kubernetes
- Remote access: Every VirtualServer gets a Tailscale ingress automatically
What’s Next?
- Monitoring: Prometheus + Grafana
- Backup: CronJobs for etcd and vault data
- GPU Passthrough: See my k8s-setup repo for GPU worker node documentation
- More Apps: Jellyfin, Home Assistant, Nextcloud
Feel free to explore my homelab repository for complete configurations!
| ← Part 1: Setting up the Kubernetes cluster | ← Part 2: Core Infrastructure and Tools |

